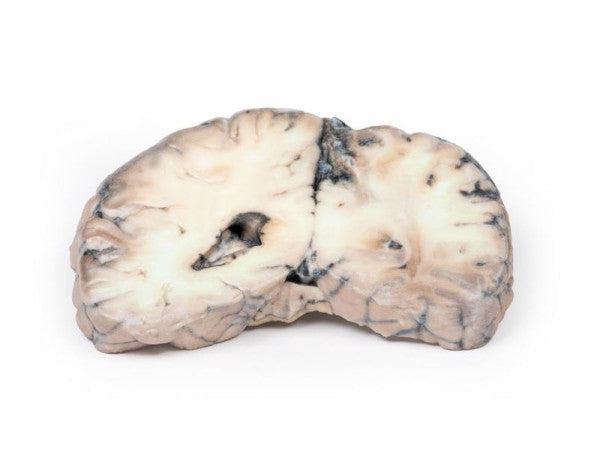
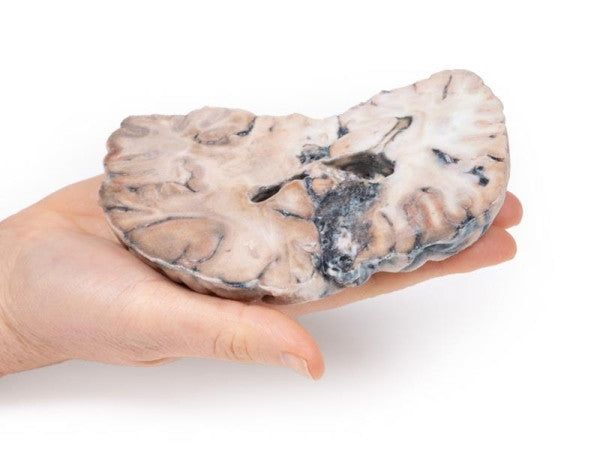
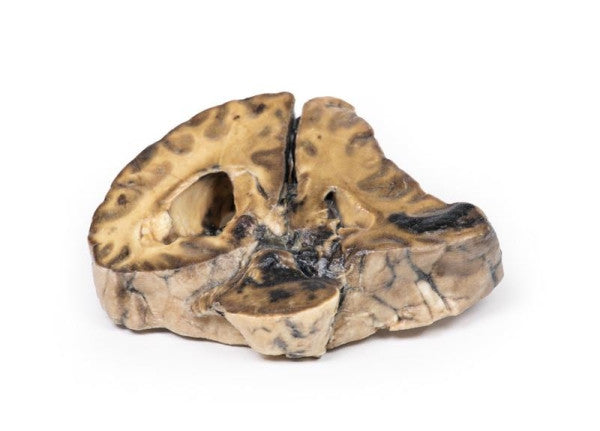
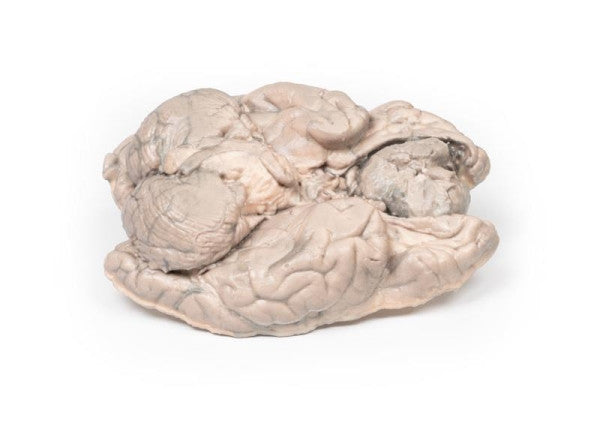
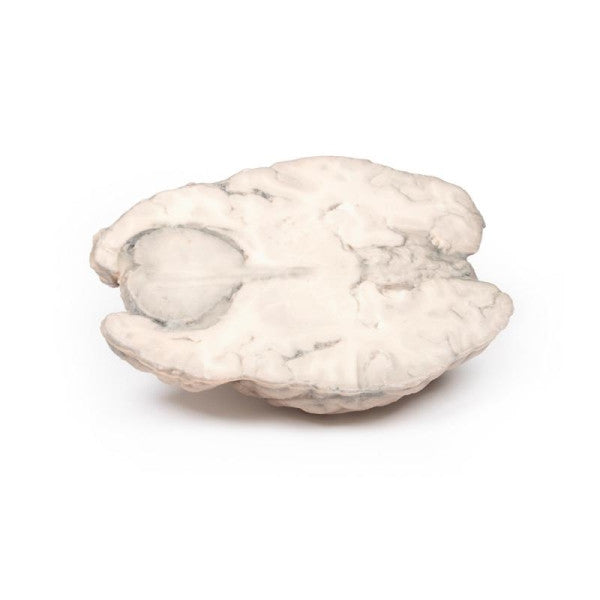
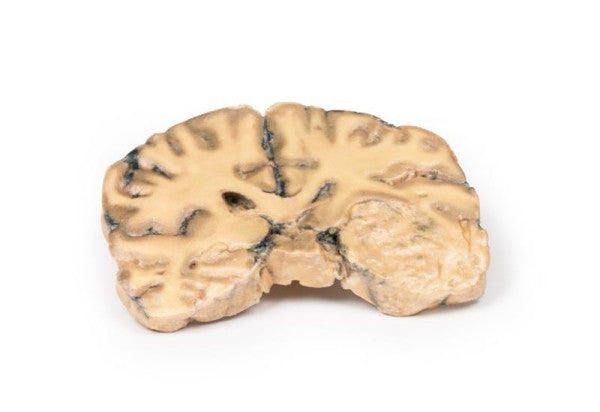
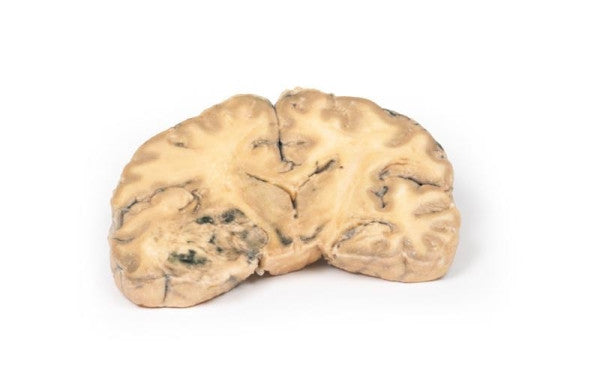
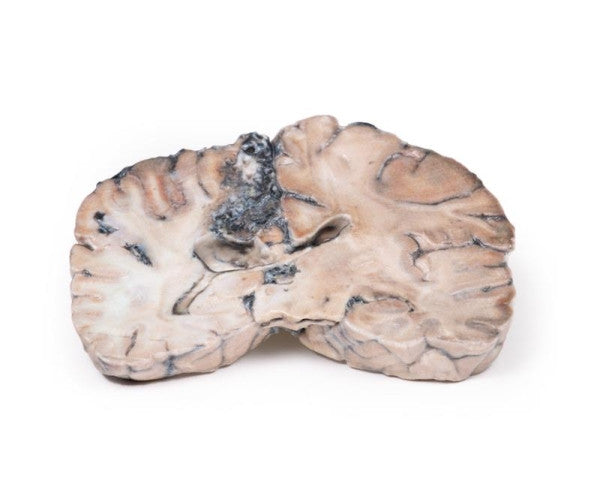
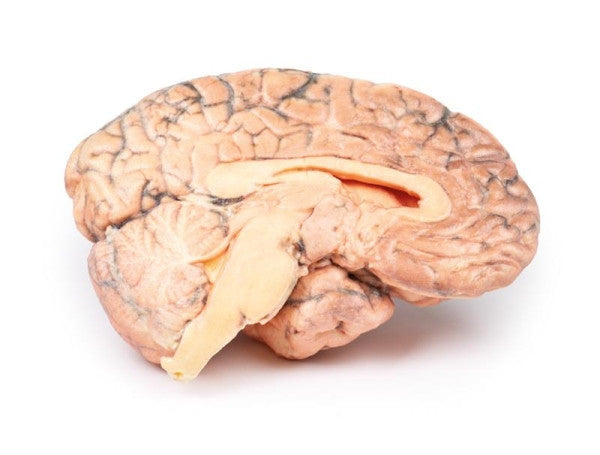
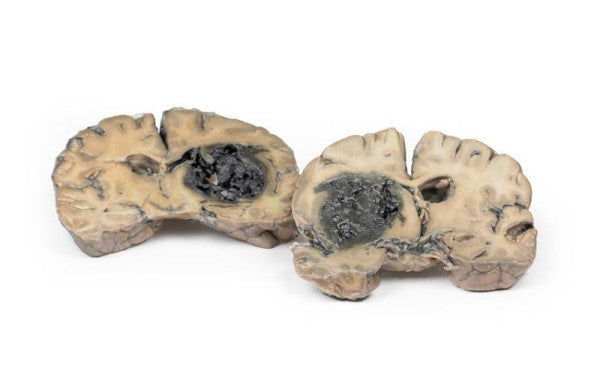
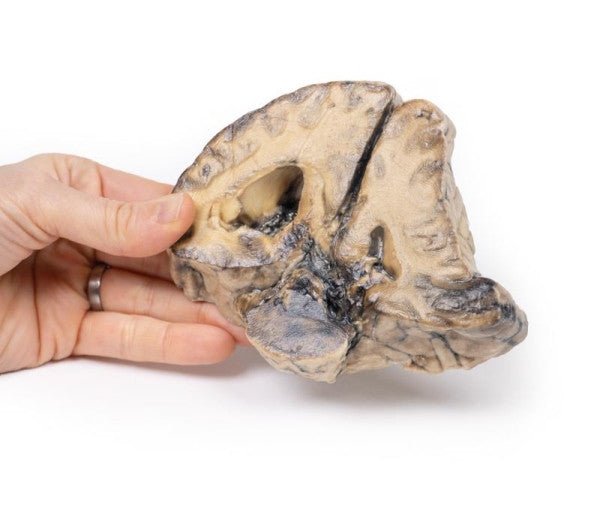
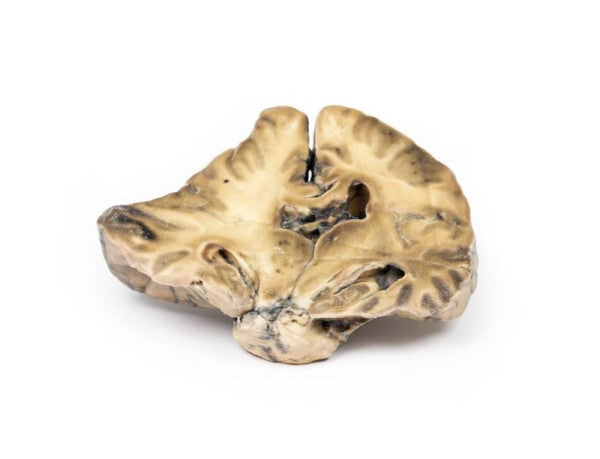
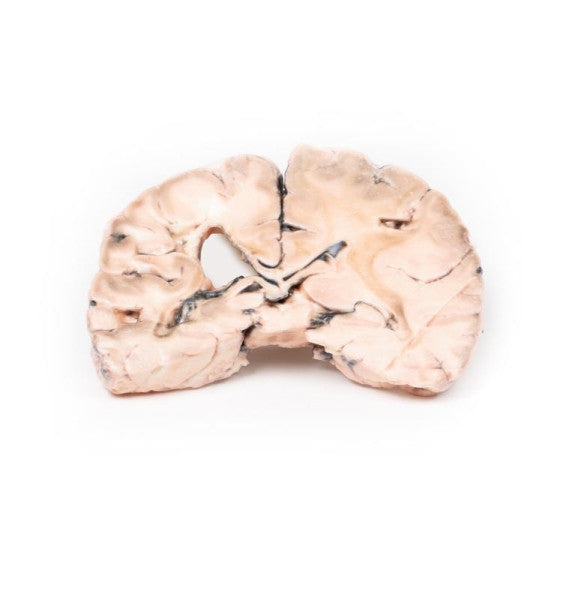
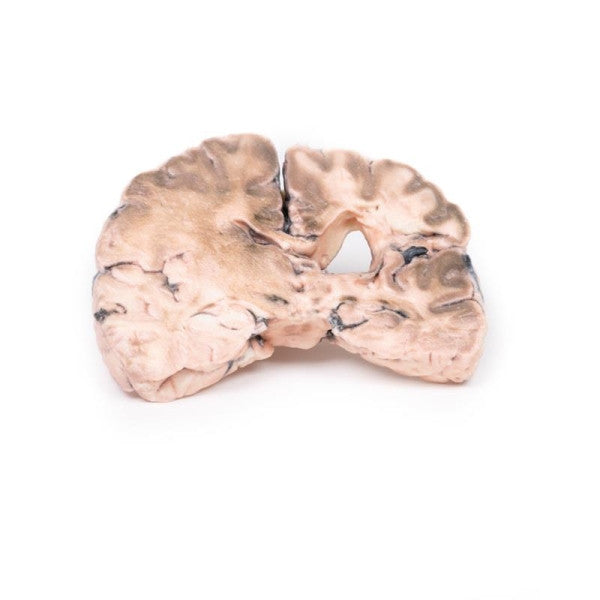
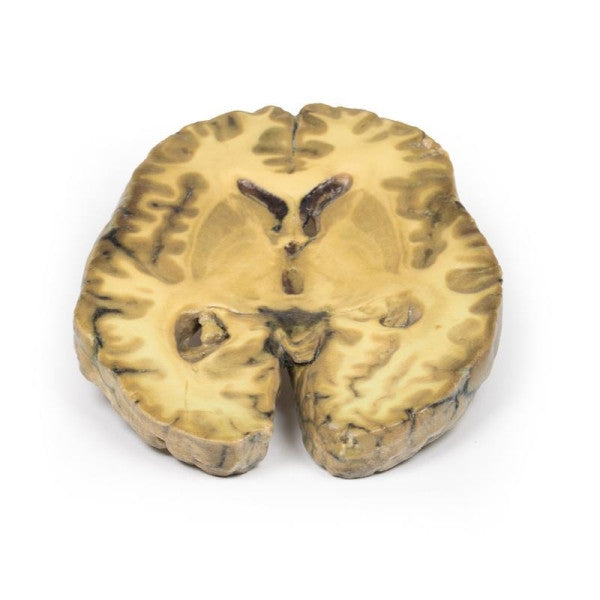
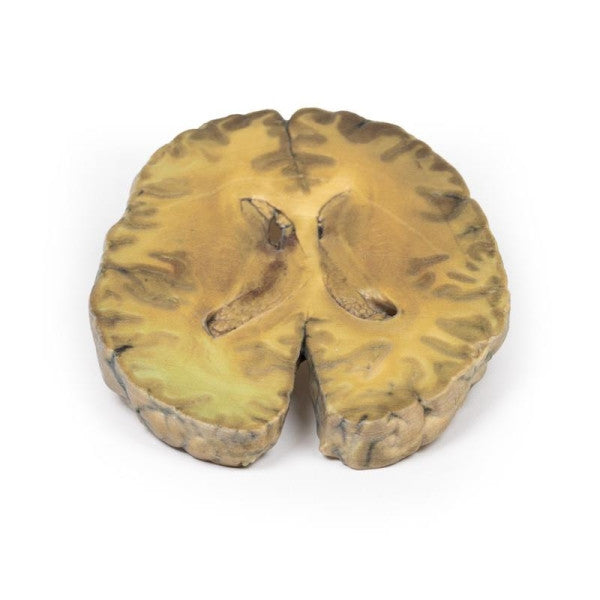
Astrocytoma
This brain specimen, depicted in a coronal section, reveals an ill-defined tumour in the right temporal lobe, leading to hemisphere enlargement and gyral pattern flattening. Subfalcine herniation is evident from the posterior aspect, and the tumour displays less differentiation with haemorrhagic and necrotic areas. Histologically, the tumour is identified as a Grade III/IV astrocytoma.
Cerebral Arterio-Venous Malformation
The coronal brain slice shows a 4cm abnormal tissue mass in the right cerebral hemisphere, replacing cortex and white matter. Histological examination identifies it as an arterio-venous malformation with dilated vessels surrounded by glial tissue, featuring variations in endothelial lining and wall thickness, distinguishing arteries and veins.
Craniopharyngioma
This sagittal brain section reveals a pink-grey tumour in the hypothalamic region, encapsulated except at the ventral pole. The tumour distorts the third ventricle, obliterating the Foramen of Munro. Caudal displacement of the optic chiasm is evident, and ventriculo-atrial shunting has prevented lateral ventricle dilation despite obstruction.
Intracerebral Haemorrhage
The brain sections show a blood clot replacing cerebral tissue in the left basal ganglia and internal capsule, originating there and rupturing into the left lateral ventricle. The right ventricle contains blood, but its walls are intact. The clot acts as a space-occupying lesion, expanding the left hemisphere, causing midline structure shift to the right. Subfalcine herniation of the left cingulate gyrus is evident.
Intracranial Space-occupying Lesion
The brain section reveals lateral and downward compression due to a right-sided intracranial mass, likely a meningioma. The midline structures have shifted anteriorly, indicating subfalcine herniation. The posterior view displays haemorrhage of different ages in the temporal lobe and pons, characteristic of supratentorial mass lesions, along with ventricular asymmetry.
Left Cerebral Infarct
A coronal brain section reveals irregular cystic cavities in the area supplied by the right middle cerebral artery. The infarcted cavities have uneven, yellow walls with partial collapse. Compensatory dilation of the left lateral ventricle is observed. The arteries below the mammillary bodies on the posterior aspect exhibit moderate atheromatous changes.
Meningioma
This brain specimen is horizontally sectioned, revealing a clearly defined 6cm tumour located between the frontal lobes. The tumour, identified as a meningioma, exerts pressure on the frontal lobes and exhibits a pinkish-cut surface with areas of yellow indicative of necrosis.
Ventriculitis, Secondary to Septicaemia
This specimen shows ventriculitis, pneumococcal meningitis, and right basal pneumonia. The horizontal section reveals changes in the lateral ventricles and surrounding structures, with histology indicating severe inflammation and damage extending into the cerebral parenchyma.