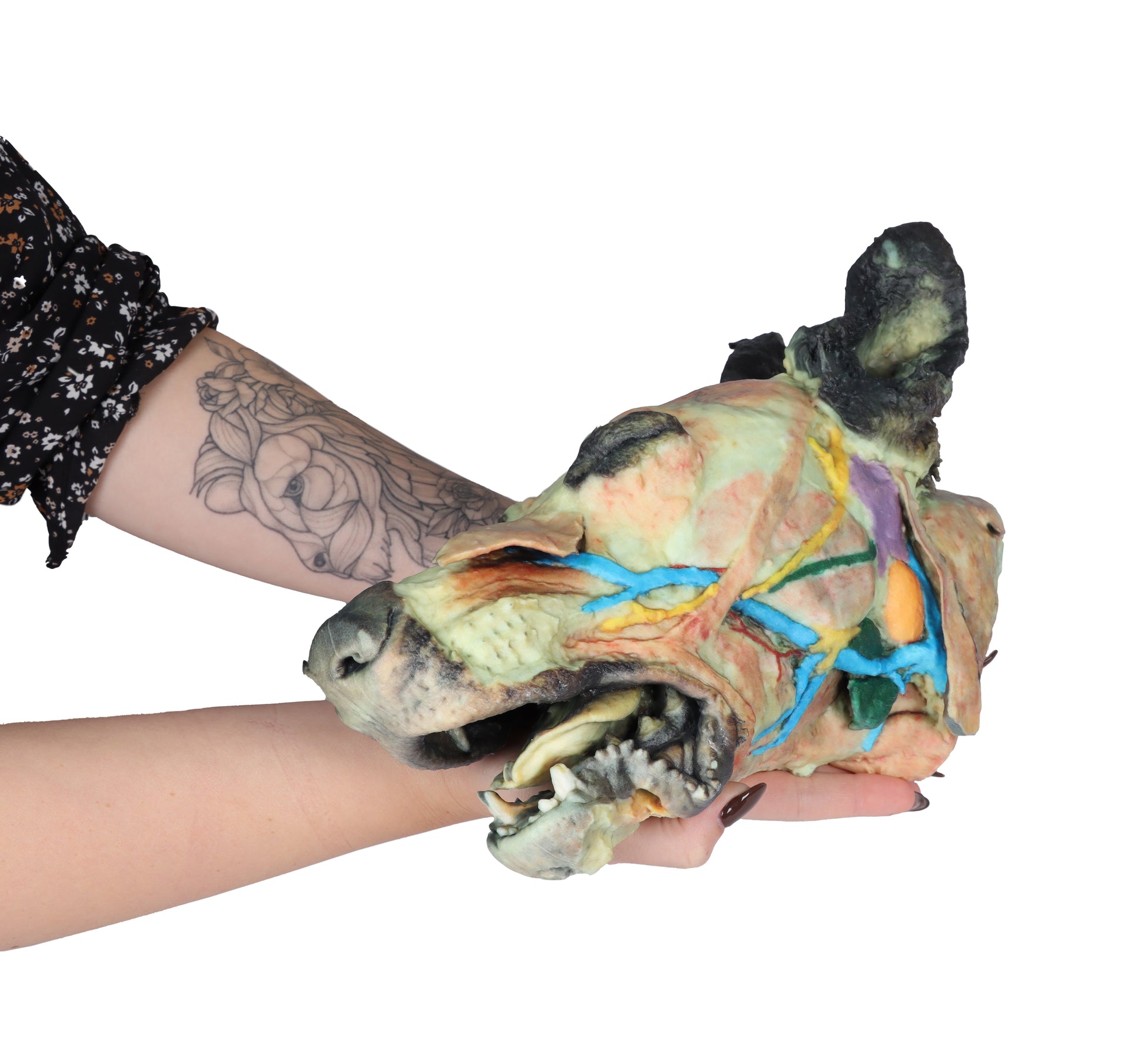
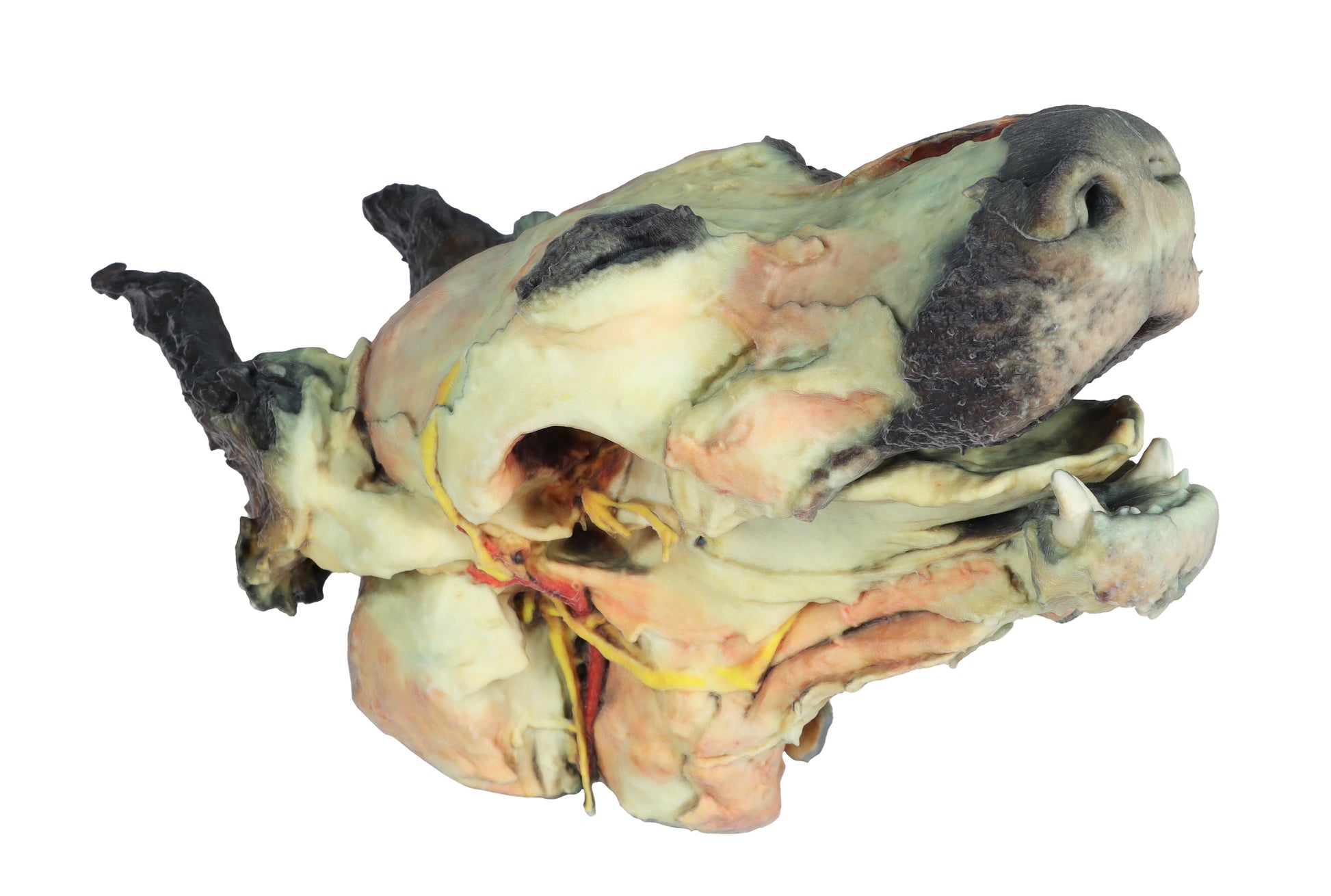
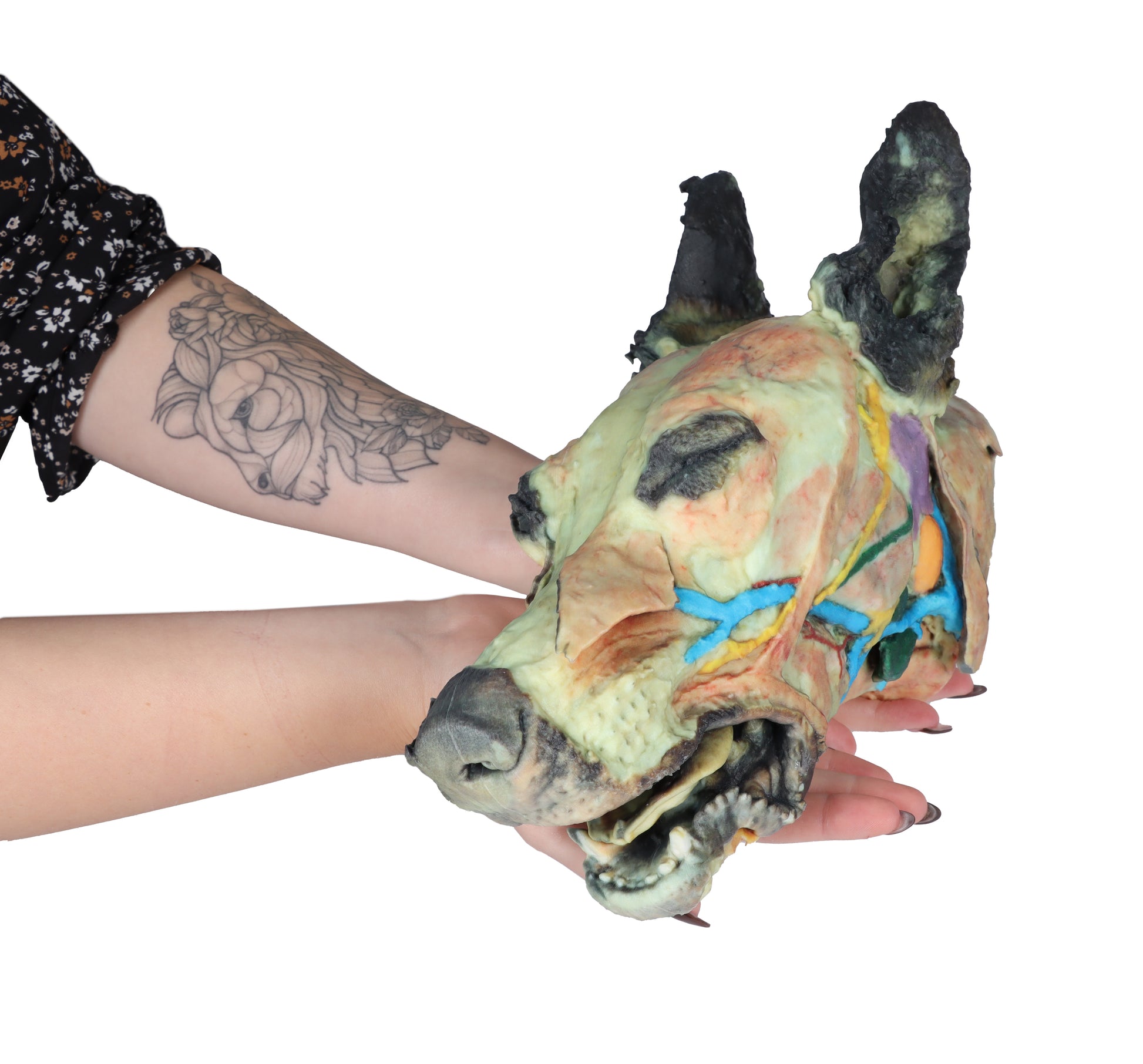
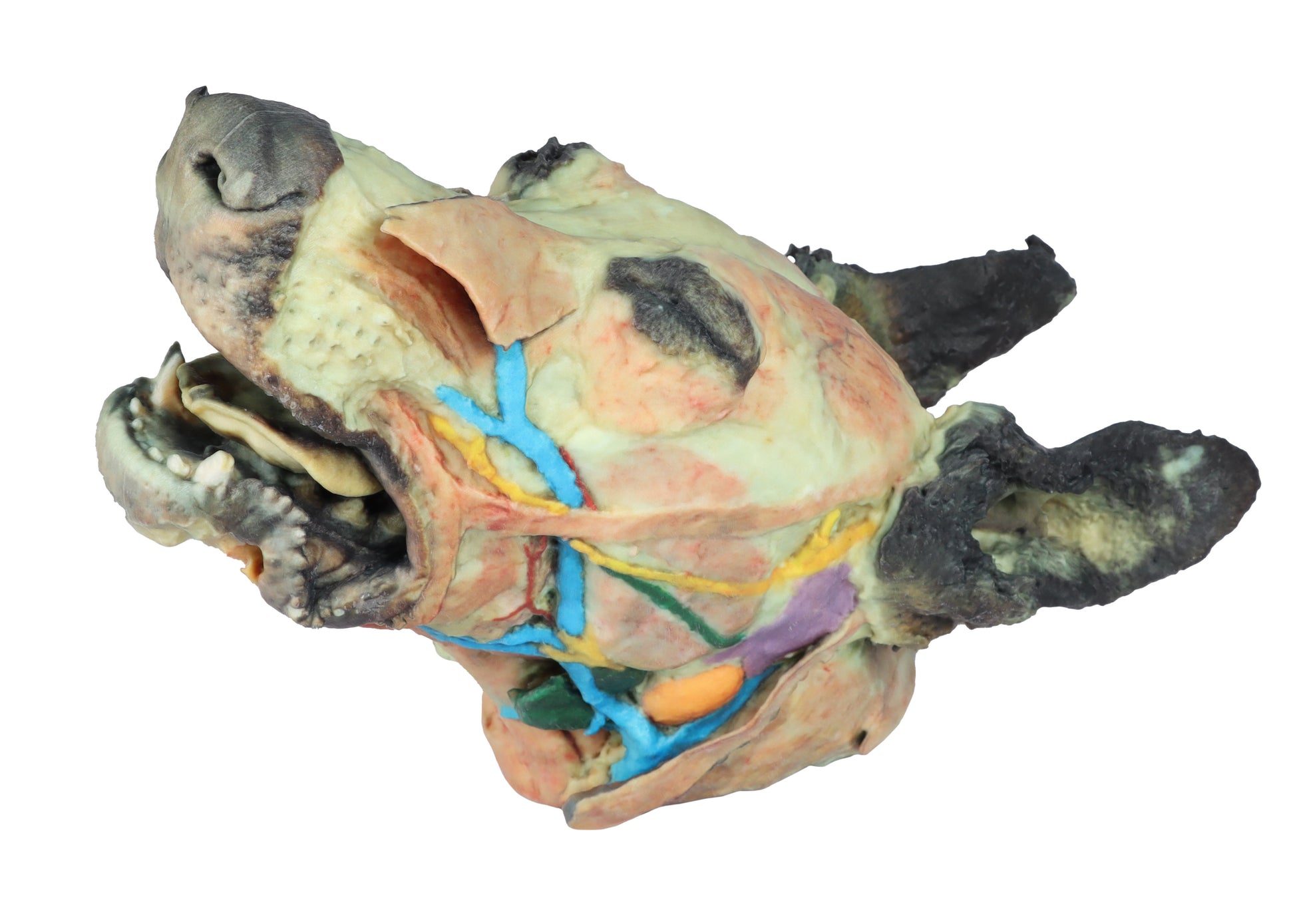
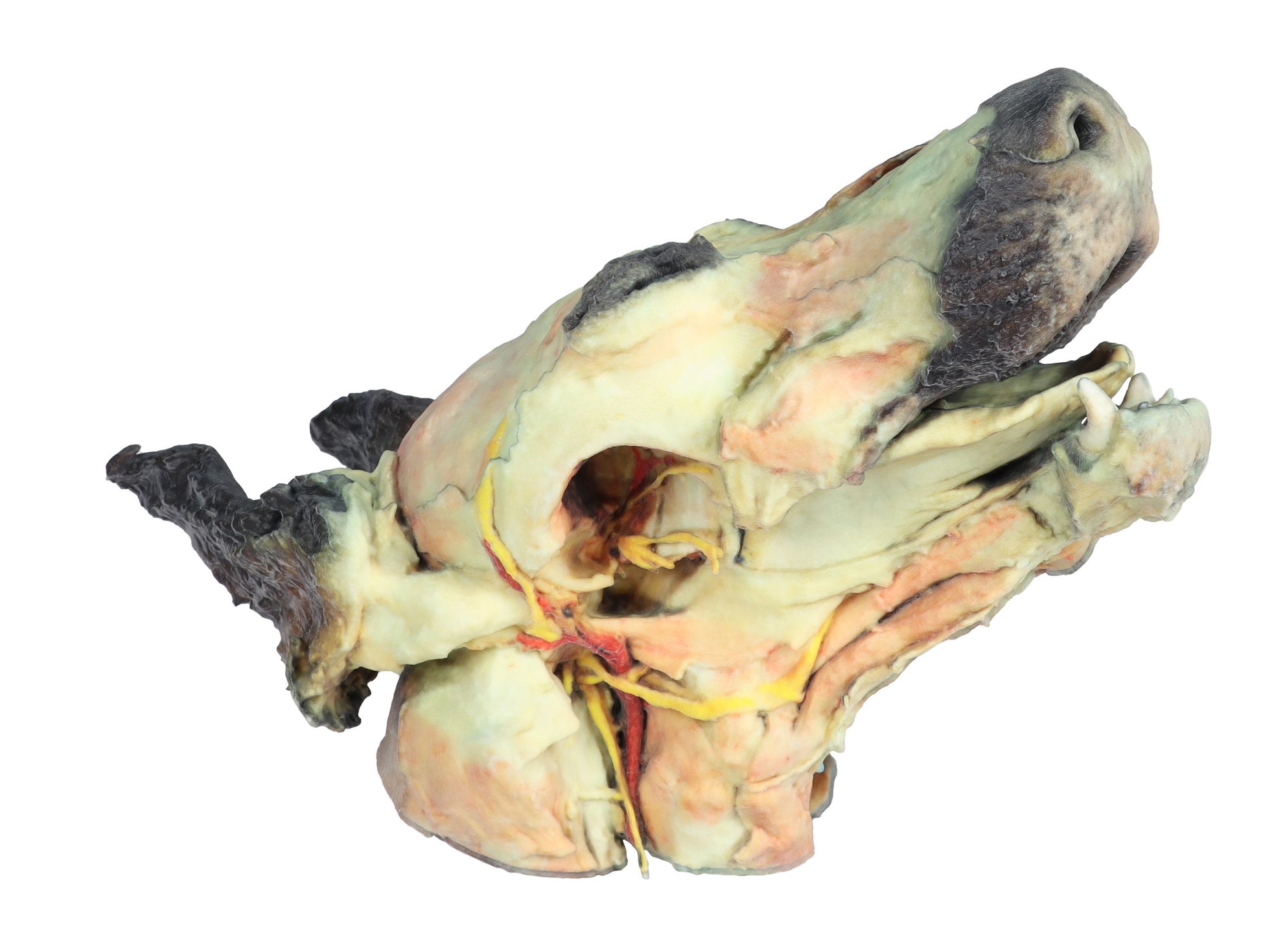
This 3D Printed Canine Head Model displays a number of anatomical structures through superficial and deep dissections.
Superficial anatomical structures include:
- Tip of the nose (Apez nasi)
- Right and left wings of the nose (Alae nasi)
- Nonglandular skin on the tip of the nose (Planun nasale)
The skin on the left side has been removed to expose the main anatomical structures which are described grouped below
Muscles of the facial neuromuscular system:
- M. nasolabial levator (M. levator nasolabialis)
- M. canine (M. caninus)
- M. buccinator (M. buccinator)
- M. Zygoma9c (M. zygoma:cus)
- M. parodidoauricularis
- Muscles of the mandibular neuromuscular system (mas9cators):
- M. masseter (M. masseter)
- M. Temporary (M.temporalis)
Nerves:
- Facial nerve (N . facialis)
- Dorsal buccal Branch (Rami buccales)
- Ventral buccal Branch (Rami buccales)
- Bucolabial branches (Rami buccolabiales)
- N. Auriculopalpebral (N. Auriculopalpebralis)
Vascular:
- Facial artery (Arteria facialis)
- External jugular vein (V. Jugularis externa)
- Maxillary vein (V. Maxillaris)
- Linguofacial vein (V. Linguofacialis)
Salivary glands:
- Parotid gland and parotid duct (Glandula parotis) (Ductus parotideus)
- Mandibular gland Glandula mandibularis
- Lymph nodes:
- N. L. mandibular (Lymphonodi mandubulares)
Deep dissection on the right side:
This right-side dissection reveals deep anatomical structures of the head and neck following removal of the mandible.
The surfaces of the temporal bone involved in the temporomandibular joint (Articulatio temporomandibularis) are clearly visible. The medial pterygoid muscle (M. pterygoideus medialis) has been sectioned near its insertion on the mandibular ramus (Ramus mandibulae), exposing adjacent neurovascular structures.
Branches of the mandibular nerve (N. mandibularis), along with the maxillary nerve (N. maxillaris) and maxillary artery (A. maxillaris), are identified in close proximity. Near the external acoustic meatus (Meatus acusticus externus), the facial nerve (N. facialis) is preserved, with its auriculopalpebral branch (N. auriculopalpebralis) visible running parallel to the zygomatic arch (Arcus zygomaticus), following removal of the parotid salivary gland (Glandula parotis).
The full caudal extent of the tongue is displayed, along with the associated muscles: styloglossus (M. styloglossus), genioglossus (M. genioglossus), and geniohyoid (M. geniohyoideus). Nearby, the hypoglossal nerve (N. hypoglossus) is also identified.
In relation to the pharynx (Pharynx), the caudal pharyngeal constrictor muscles (Mm. constrictores pharyngis caudales) are visible. At the caudal end of the specimen, near the neck, both the common carotid artery (A. carotis communis) and the vagosympathetic trunk (Truncus vagosympathicus) are clearly demonstrated.
This model is part of a range of detailed 3D printed veterinary models, exclusively available in the UK via AnatomyStuff, ideal for advanced anatomical study.